# API Playground Overview
The API Playground section contains swagger pages that allow you to see all of the ABB Ability Platform™ endpoints in a visual way. The purpose of the playground is to get you familiar with the Ability Platform functionalities by easy experimentation with the endpoints.
Ability Sandbox
API Playground has many restrictions due to its shared-with-everyone nature (more on that below). If this is not acceptable for your PoC/experimentation, have a look at Ability Sandbox.
If you have access to your own Sandbox environment, you can continue to use API Playground in the context of that Sandbox environment. Just change the tenant name to your own in the API page (click the "Access your Sandbox environment" dropdown).
Webinars
We recommend you to watch the following recording to gain a better understanding of the topic:
The listing of all webinars can be found here
# Using the Playground
The API Playground can be used in three ways:
- without an access to the Ability Platform
- with access to the Ability Platform, as a "standard" user
- with access to the Ability Platform, as a user of the Sandbox
# Without an access to the Ability Platform
You will see what endpoints are available, but you will not be able to execute any of them successfully (more precisely, you will get HTTP 401 (Unauthorized) response for every request).
# With an access to the Ability Platform, as a "standard" user
You will be able to explore APIs interactively - all your requests will be sent to an actual Ability Platform running in the cloud. Note that all of the users of the playground will use the same instance and a single tenant of the platform.
TIP
The Ability Platform beneath the API Playground is the latest released version of the platform.
WARNING
Only API Playground has access to a live instance of Ability Platform. Region API and Global API Playgrounds do not have access to Ability Platform, due to the amount of restrictions that this would require on a shared environment.
Some key points:
- Do not input any sensitive data into the playground
- Expect to find data that was not created by you
- Expect the data you fed to be deleted anytime
- Expect to hit some restrictions:
- You cannot delete
abb.ability.deviceandabb.ability.configurationmodel definitions - You cannot access endpoints that are accessible only by background applications (Reingestion API)
- you cannot modify the data that is presented in the Usage Examples) section of this page
- you cannot use the "Encryption Keys" endpoint
- API Playground does not allow connecting devices to the platform
- You cannot delete
TIP
Your are able to access Ability Platform this way any time you want. It's free of charge.
# With an access to the Ability Platform, as a user of the Sandbox
If you own a Sandbox environment, you may access it by using API Playground. To do that, go to the API page, and click the dropdown:
You will see a text input that allows you to change the tenant that you want to log into. By default, users are logged into the API Playground Tenant. As a user of this tenant you will not be able to access the data in your Sandbox environment. To change that, input the name of your private tenant (you received this name in the e-mail with sandbox environment details).
Then, click the "Get Access to the Playground" button.
From now on, any operation that you invoke will be executed in the context of your Sandbox Environment. You will be able to access your objects, telemetry, invoke commands on your devices, and so on.
WARNING
You will be able to access the Ability Platform this way until your Sandbox environment is still valid.
# Prerequisites of accessing Ability Platform
In order to access API Playground, any of the below requirements must be satisfied:
- Client computer utilizes Ability VPN while connecting to ADP
- Client computer has the iboss Proxy server installed and used while connecting to ADP
Security rules established for Ability Resources are described in:
Information about how to request Ability VPN installation can be found in article: VPN Request in Service Now
# Usage Examples
Since the API Playground is connected to the actual Ability Platform, you are able to CREATE/WRITE/READ/DELETE the data. Below are some examples of API calls that you might try to make.
TIP
These examples are to be used only by the "standard" users. If you are logging into the Playground with your Sandbox environment tenant, you will not see the objects and telemetry that are shown in the examples. You will only be able to see the data that you have created in your private environment!
# Type Definition
Note that there is an exemplary type definition that is available at all times. API Playground users have no permission to modify it.
abb.ability.playground.motor
{
"model": "abb.ability.device",
"typeId": "abb.ability.playground.motor",
"version": "1.0.0",
"properties": {
"serialNumber": {
"dataType": "string"
}
},
"variables": {
"voltage": {
"dataType": "number",
"unit": "V"
},
"current": {
"dataType": "number",
"unit": "A"
}
}
}
You can check it out yourself by invoking the GET edpoint in the Type Definitions category:
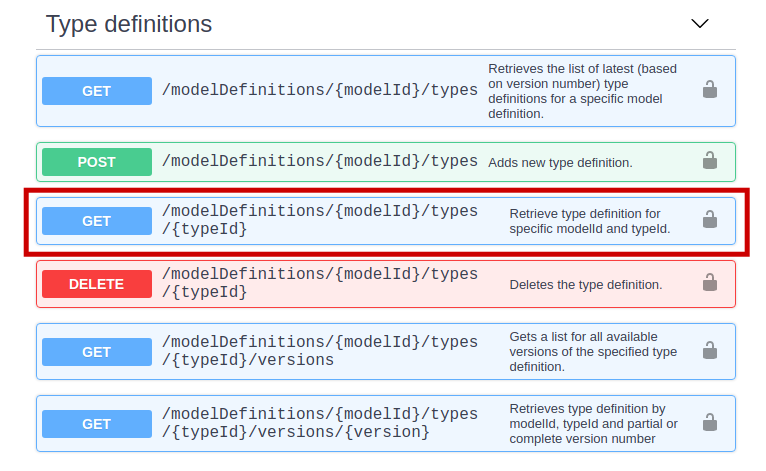
The parameters that you need to specify are as follows:
- modelId: abb.ability.device
- typeId: abb.ability.playground.motor
When you execute the request, you should see the type definition.
# Object Models
Based on the type definition shown above, there are three object models that you can inspect (objectIds):
22ab830b-6fc6-4bf5-9579-8ae38088074a48d17460-7416-4f10-b40a-47da69e5e568a0b2b173-a66a-4329-9583-7abf8f97637e
To see them, execute the GET request in the Objects category:
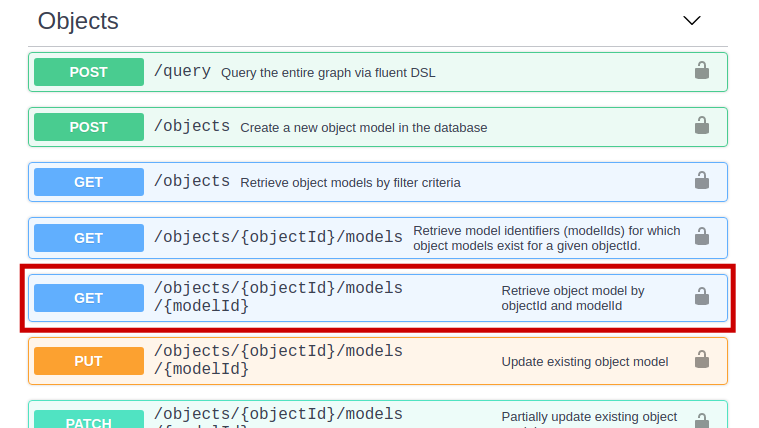
The parameters that you need to specify are as follows:
- objectId: {one of the above obejctIds}
- modelId: abb.ability.device
You will get the JSON representation of the chosen object model, like this:
{
"model": "abb.ability.device",
"type": "abb.ability.playground.motor@1",
"version": 1,
"lastModified": "2020-12-08T13:41:20.632Z",
"properties": {
"serialNumber": {
"value": "motor #1"
}
},
"objectId": "22ab830b-6fc6-4bf5-9579-8ae38088074a",
"tenantId": "f4831d89-9f60-471a-b063-5fbcda46584b"
}
TIP
Nothing stops you from creating your own object models. The three pre-created object models are just an example.
# Timeseries Data
API Playground does not allow you to write any timeseries data into the platform, because that would require some major changes in the permission set that the users get. However, we have prepared some demo data so that you ca still check the Variable Query endpoint. The data was created for the same three objectIds that we presented above, in the Object Models section. Both "voltage" and "current" variables were filled with data. The timeframe that the data is available in is: 10th December 2020 00:00:00 - 11th December 2020 00:00:00. The time interval between subsequent data points is 10 seconds. It means that for each object-variable pair, you will find 8640 data points.
To query for variables data, use this endpoint in the Data section of API:

This endpoint is a POST one. The example of the request payload could be:
{
"date": {
"from": "2020-12-10T15:00:00.000Z",
"to": "2020-12-10T16:00:00.000Z"
},
"filter": "objectId='22ab830b-6fc6-4bf5-9579-8ae38088074a' AND variable='voltage'",
"orderBy": {
"property": "timestamp",
"order": "asc"
},
"limit": 3
}
This way, you'd get only the values of voltage for object 1922c5e6-5cea-42b3-af57-817e58d45bab, in the timeframe of 2020-12-10T15:00:00 - 2020-12-10T16:00:00. The data will be sorted chronologically, and maximum 3 values will be returned. Here's the response:
{
"data": [
{
"objectId": "22ab830b-6fc6-4bf5-9579-8ae38088074a",
"model": "abb.ability.device",
"timestamp": "2020-12-10T15:00:00Z",
"variable": "voltage",
"value": 72.6746664720935
},
{
"objectId": "22ab830b-6fc6-4bf5-9579-8ae38088074a",
"model": "abb.ability.device",
"timestamp": "2020-12-10T15:00:10Z",
"variable": "voltage",
"value": 70.2066450706714
},
{
"objectId": "22ab830b-6fc6-4bf5-9579-8ae38088074a",
"model": "abb.ability.device",
"timestamp": "2020-12-10T15:00:20Z",
"variable": "voltage",
"value": 82.4355021502988
}
]
}
TIP
For more examples of how to query "warm" data, look at this article.
# Other Examples
The shown examples are just a few of the possible requests you can make. Feel free to experiment more by creating your own model definitions, type definitions, and objects. You can then update them, create references between them, etc. Feel free to experiment!
